See Explanation
[ "https://i.postimg.cc/SNBvwCjy/case-104930-image-1-leprosy.jpg", "https://i.postimg.cc/9QynV0qy/case-104930-image-2-tuberculoid-leprosy-mp.jpg" ]
Infectious
bacterial disease
mycobacterial infections
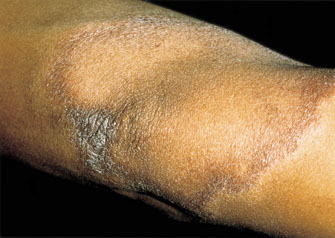
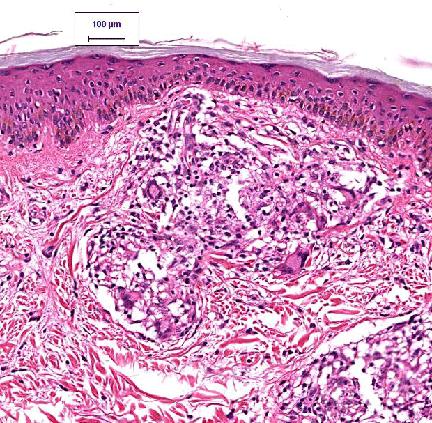
A 50-year-old male, recently arrived from a region known for endemic infectious diseases, presents to an outpatient clinic for a follow-up visit. He was initially seen for an unrelated complaint, but during the physical examination, a raised, erythematous plaque measuring approximately 6 cm in diameter was noted on his left elbow, which he reported as being present for several months. Upon further inquiry, he mentions a long-standing decrease in sensation over this area. Physical examination reveals complete anesthesia to light touch and pinprick over the lesion and extending distally. There is also a palpable thickening of the ulnar nerve proximally to the lesion. A biopsy performed during his last visit confirmed granulomatous inflammation with evidence of acid-fast bacilli. His recent laboratory work-up is detailed below. Given the clinical presentation and biopsy findings, what is the most appropriate multi-drug therapy regimen, and what long-term neurological complication should be actively monitored?
| Lab Parameter | Value | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| White Blood Cell Count | 8.2 x 10^9/L | 4.0-11.0 x 10^9/L |
| Hemoglobin | 14.5 g/dL | 13.0-17.0 g/dL |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) | 38 mm/hr | <20 mm/hr (for males <50 years) |
Edit question